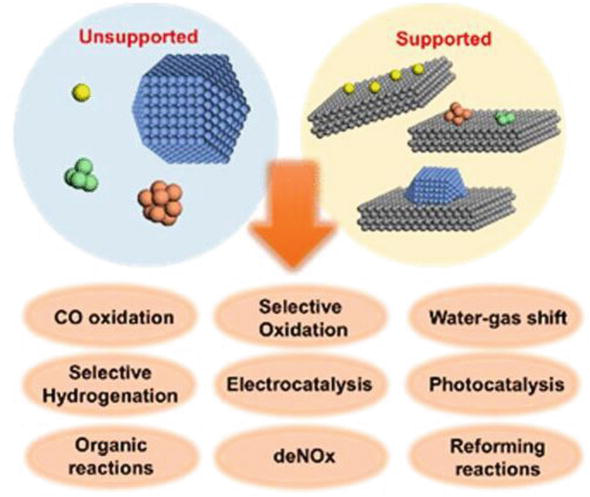
√100以上 homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis examples 333700-Define homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis with examples
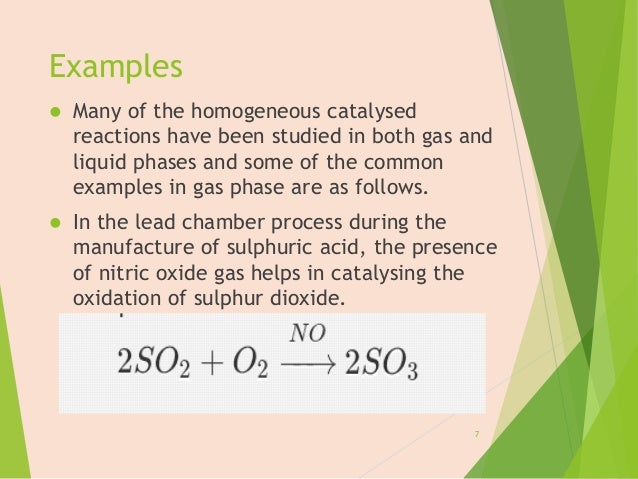
Enzymes are homogeneous catalysts that are essential for life but are also harnessed for industrial processes A wellstudied example is carbonic anhydrase, which catalyzes the release of CO 2 into the lungs from the bloodstream Enzymes possess properties of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts As such, they are usually regarded as a third,Enzymes are homogeneous catalysts that are essential for life but are also harnessed for industrial processes A wellstudied example is carbonic anhydrase, which catalyzes the release of CO 2 into the lungs from the bloodstream Enzymes possess properties of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts As such, they are usually regarded as a third, separate category of (a) Homogeneous Catalysis When the catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants, the phenomenon is called homogeneous catalysis For example (i) Nitric oxide catalyses the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in the lead chamber process (ii) Hydrogen ions catalyse the inversion of cane sugar (b) Heterogeneous Catalysis

Which Of The Following Reactions Is An Examples Of Homogeneous Catalysis Youtube
Define homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis with examples
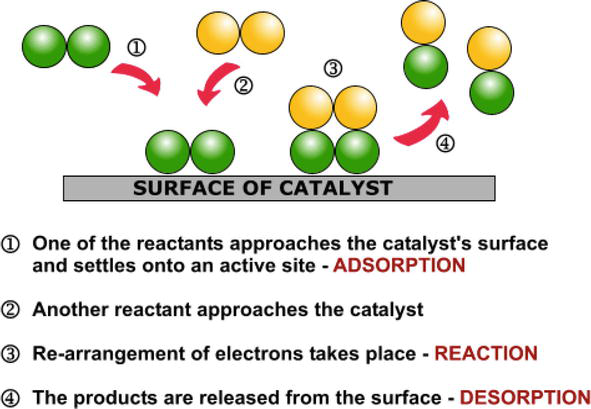
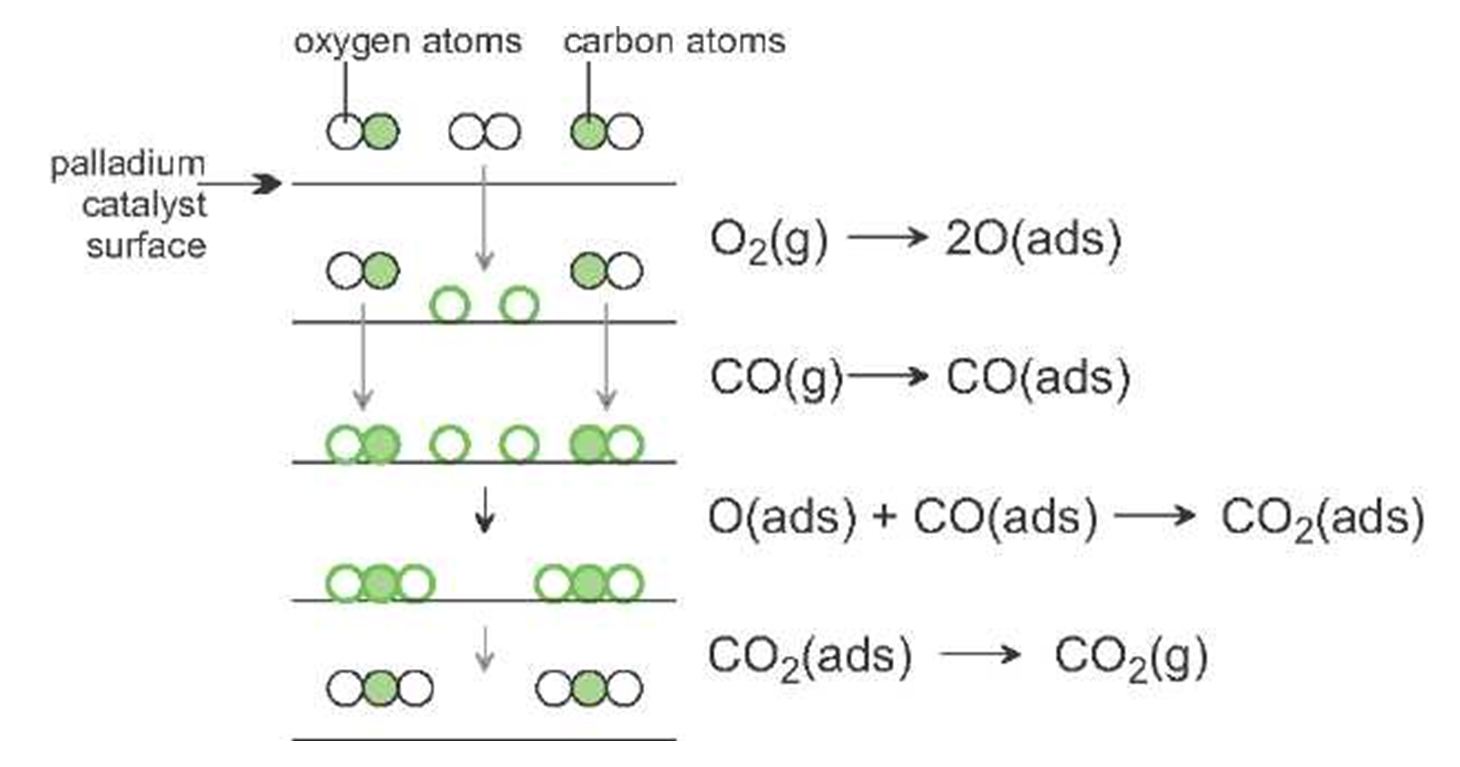
Define homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis with examples-Homogeneous Catalysis Homogeneous catalysis of chemical reactions is a process where the reactants involved in the reaction and the catalyst are in the same phase For example hydrolysis of sugar in the presence of sulphuric acid Heterogeneous Catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis of chemical reactions is a process where the reactants involved in the reaction and the catalyst are in different phases For exampleFor example, the combination of SO 2 and O 2 to form SO 3 is a slow process However, in the presence of NO (catalyst), the reaction becomes fast Fig 2 Step 1 Adsorption, Step 2 and 3 Reaction, Step 4 Desorption Step 1 Diffusion of the reactants at the surface of the catalyst



Homogeneous Catalysis Mpharm Msc Bpharm Bsc
Some common examples of reactions that involve heterogeneous catalysis (reactions in which the physical states of the reactants and the catalysts are different) are provided below The contact process for the synthesis of sulfuric acid, which involves the reaction between oxygen and sulfur dioxide, catalyzed by oxides of vanadium Heterogeneous catalysis is a type of catalysis in which the catalyst occupies a different phase from the reactants and products This may refer to the physical phase — solid, liquid or gas — but also to immiscible fluids Heterogeneous catalysts can be more easily recycled than homogeneous, but characterization of the catalyst andExamples of homogeneous catalysis The reaction between persulphate ions and iodide ions This is a solution reaction that you may well only meet in the context of catalysis, but it is a lovely example!
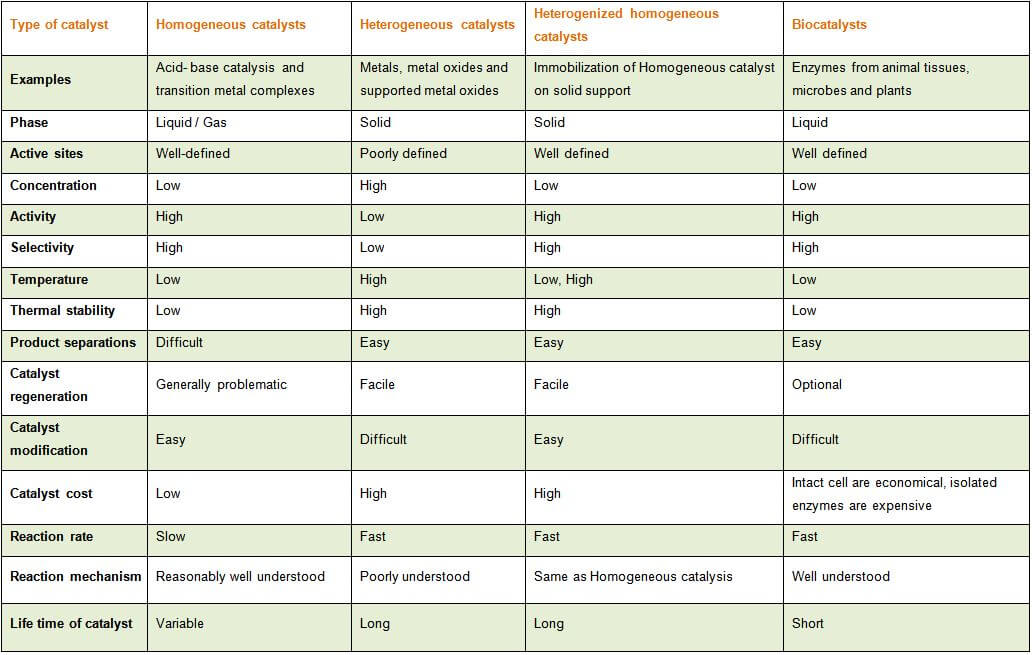
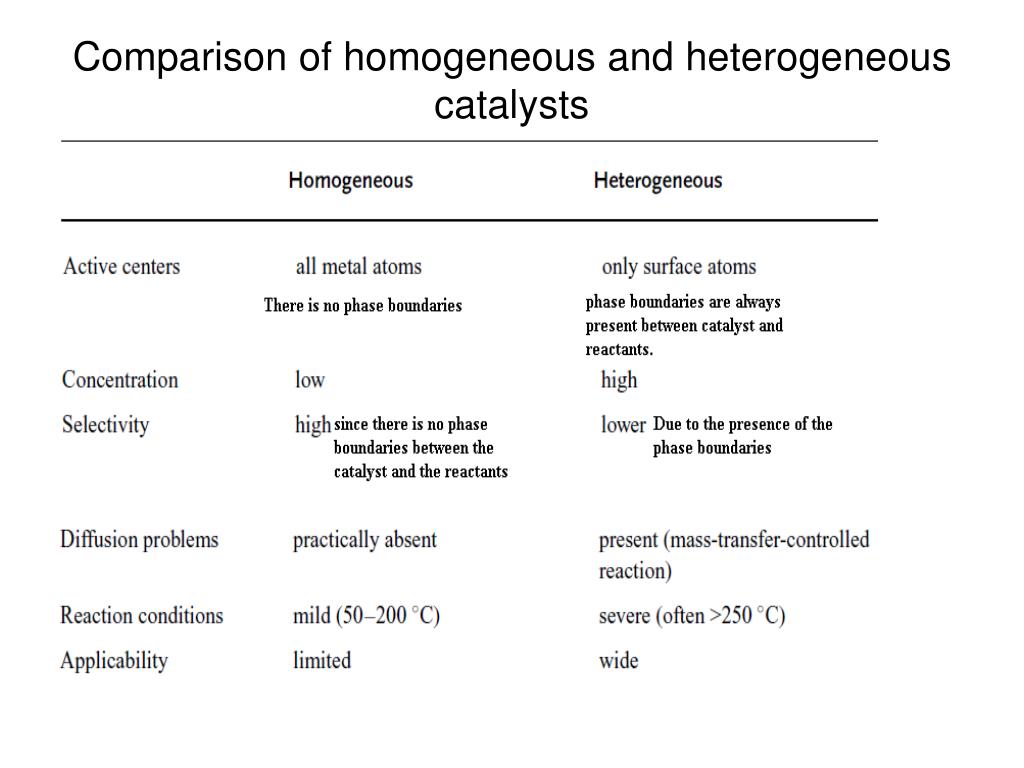
The heterogeneous catalysts over the homogenous as it makes the separation e reutilization of heterogeneous catalysts simple and cheap compared to the homogenous catalysts A great variety of homogeneous catalysts are known, ranging from Brønsted and Lewis acids widely used in organic synthesis, metal complexes, metals ions, organometallicTable 1 compares homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis in terms of catalytic effectiveness, catalyst properties, and catalyst separation1 Homogeneous catalysts offers improved selectivity, increased activity, and avoid mass transfer limitations, which may permit lower temperatures Table 1 Comparison between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis A homogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that exist in the same phase as the species involved in the reaction, and heterogeneous catalysts exist in a different phase Enzymes surve as an example of a homogeneous catalyst, they exist in solution and catalyze reactions that occur in solution
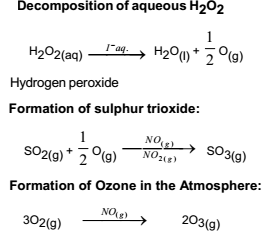
Tel 31 46 b Department of Chemistry, Joseph Black Building, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK G12 8QQUnlock the full Alevel Chemistry course at http//bitly/2ZDDPTi created by Ella Buluwela, Chemistry experHomogeneous catalysis catalysis in which the reactants and catalyst are in same phaseIe same physical state Example 2 S O 2 (g) O 2 (g) → N O (g a s) 2 S O 3 (g) Heterogeneous catalysis catalysis in which the reactants and catalyst are in phases Ie different physical states Example 2 S O ( g) O ( g) → P t (s) 2 S O 3 (g)



2




Give Four Examples Of Heterogeneous Catalysis
Homogeneous catalysts work better in lowtemperature conditions (less than 250 0 C) In which the reactants and catalyst are in a similar phase Example 2SO 2 (g) O 2 (g) —– No(g) → 2SO 3 (g) Heterogeneous catalysis Heterogeneous catalysts are catalytic compounds that are in a contradictory phase from that of the phase of the reaction combinationNitrogencontaining heterocycle to be formed by homogeneous catalysis is the triazine shown in Equation 1 which is the product of the trimerization of benzonitrile in the presence of iron penta carbonyl or Raney nickel 4 Aspects of Homogeneous CatalysisRenato Ugo 1970 Aspects of Homogeneous CatalysisR Ugo 1 INTRODUCTION In this Chem issue, Han et al devised a system relying on tandem heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis by ruthenium species for the CO 2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons with remarkable efficiency In particular, 5atom (or longer) chain hydrocarbons were obtained with remarkably high selectivity (711%)




Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Heterogeneous Catalysis All About Drugs
Acid catalysis, organometallic catalysis, and enzymatic catalysis are examples of homogeneous catalysis Homogeneous catalysts are used in variety of industrial applications, as they allow for an increase in reaction rate without an increase in temperature Click to see full answer Likewise, people ask, what is heterogeneous catalysis give examples?Emulsion catalysis has been demonstrated to be quite useful strategy for overcoming the compatibility of different media in the liquid–liquid biphasic reaction system This chapter introduces the basic concept of emulsion catalysis and its application for the oxidative desulfurization, Lewis acidcatalyzed organic reactions, organocatalyticCatalysts Homogeneous & Heterogeneous in a Snap!



Homogeneous Catalysis Mpharm Msc Bpharm Bsc




Catalysis
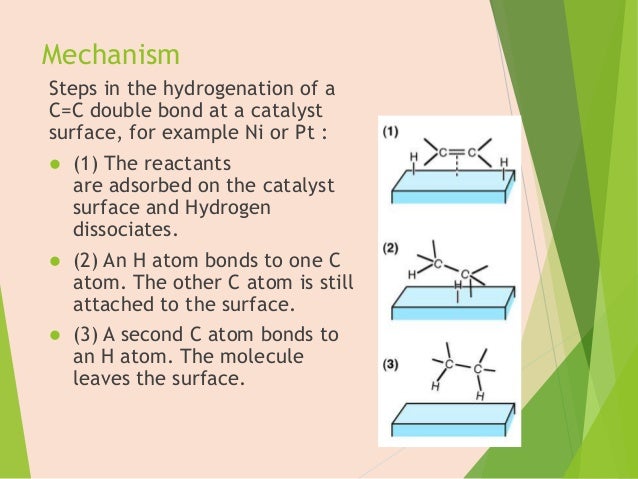
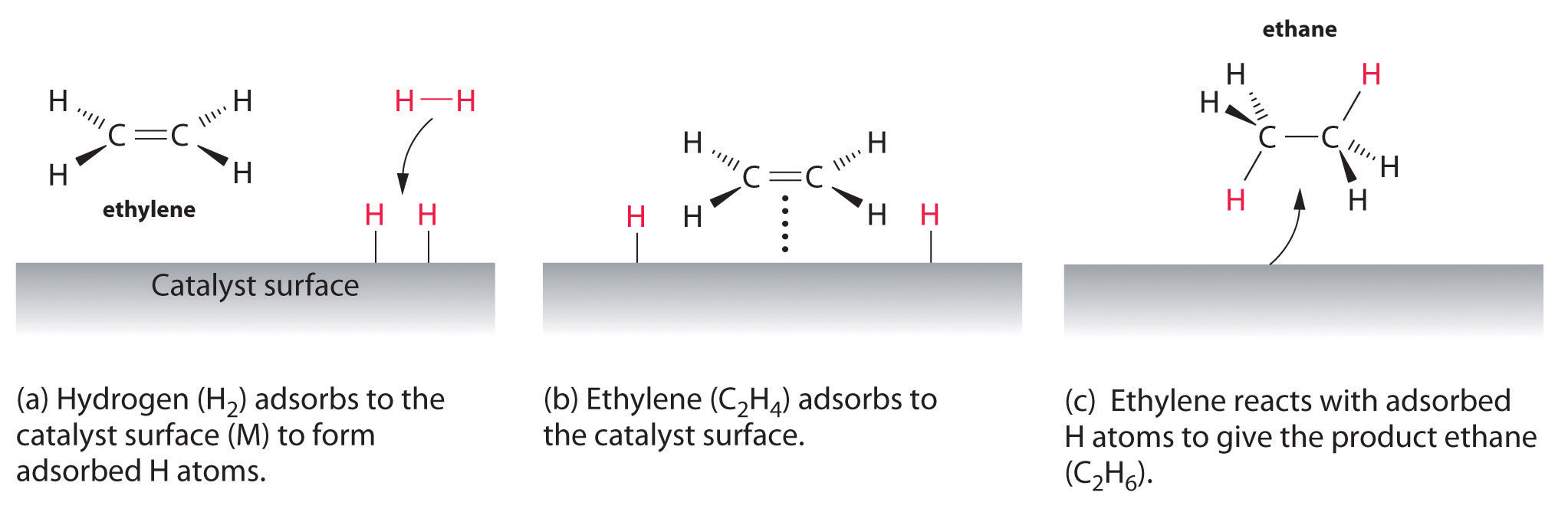
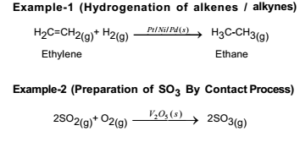
An example of heterogeneous catalysis is the interaction of hydrogen gas with the surface of a metal, such as Ni, Pd, or Pt As shown in part (a) in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) , the hydrogen–hydrogen bonds break and produce individual adsorbed hydrogen atomsTypically, heterogeneous catalysis involves the use of solid catalysts placed in a liquid reaction mixture Catalysis Note the lowered activation energy of the catalyzed pathway Examples of Homogeneous Catalysts Acid catalysis, organometallic catalysis, and enzymatic catalysis are examples of homogeneous catalysisHeterogeneous catalysts are just a tethered version of a homogeneous catalyst At the microscopic, bondbreaking, bondmaking level, usually only a few atoms close to the bond being broken/formed are critical Big practical difference is that it is easy to separate/immobilize heterogeneous catalyst Also, heterogeneous catalysts have some diffusion




Catalysts Transition Metals Secondary Science 4 All




Explain The Difference Between A Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Give An Example Of Each Youtube
The class of homogeneous catalysts is extraordinarily broad from the hydrogen () ion in acid catalyzed reactions like ester hydrolysis to natural enzymes (virtually all of them an example is carbonic anhydrase enzymes often have a metal ironDifference Between Homogeneous Catalysis and Heterogeneous Catalysis Video Lecture from Surface Chemistry Chapter of Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSHomogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis in industry Johannes G de Vries a and S David Jackson b a DSM Innovative Synthesis BV, PO Box 18, 6160 MD Geleen, The Netherlands Email HansJGVriesde@dsmcom;



Catalysis



Catalysis Meaning Of Catalyst Its Characteristics And Types
Homogeneous catalysis In a reaction, if the catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants, it is called a homogeneous catalyst and the phenomenon is homogeneous catalysis Such catalysis can take place in gaseous reaction or reactions in solution This type of catalysis can sometimes be explained in terms of the formation of an intermediate compound, or ion or a An example of a homogeneous catalysis is one wherein the catalyst and the reactants are in the gaseous phase An example is acid catalysis The acid dissolved in water produces a proton that speeds up chemical reaction, such as in the hydrolysis of estersThe esterification reaction is another wellknown example of homogeneous catalysis 7,8 In this reaction, sulfuric acid dissolves in ethanol/ethanoic acid Although in this catalysis there is a good contact with reactants, separation of the catalysis after the interaction and catalyst




Single Atom Catalysis Bridging The Homo And Heterogeneous Catalysis Sciencedirect
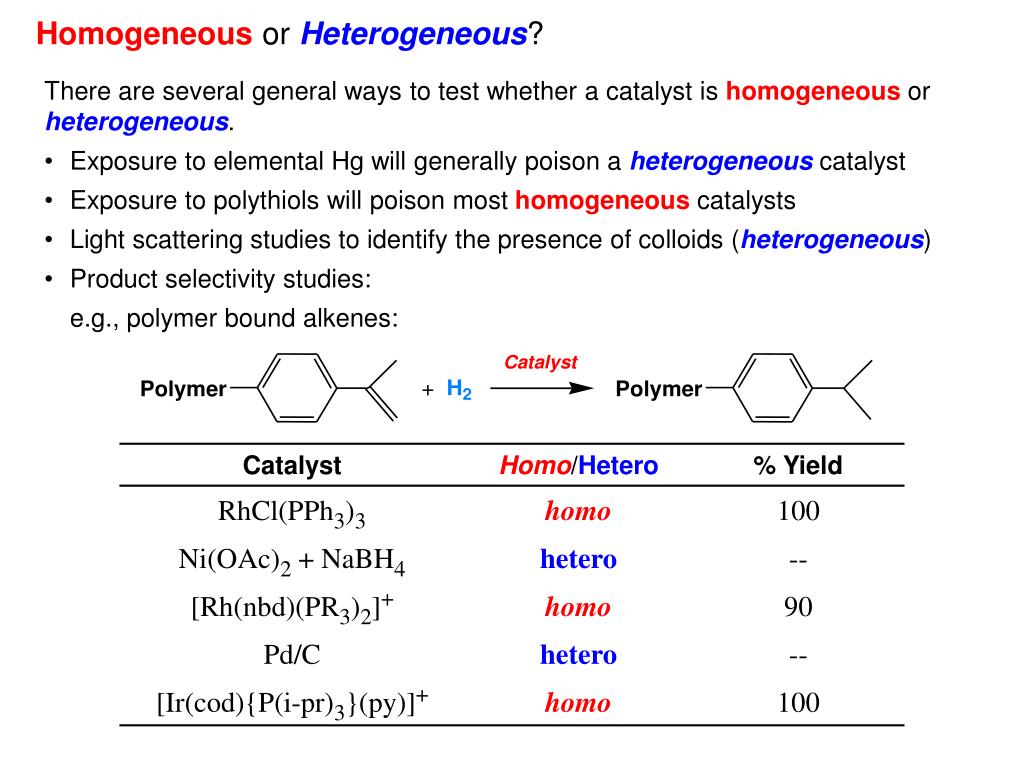



Ppt Homogeneous Catalysis Introduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2213
Heterogeneous Heat Transfer might be an issue due to the different heat capacities of reactants and catalystCatalyst Separation Homogeneous The separation of the products from the catalyst is generally expensive, the only exception being in biphasic catalysis Heterogeneous The separation of the products from the catalyst is usuallyExamples of homogeneous catalysis in the gas phase are (a) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide, SO 2, by oxygen to sulphur trioxide, SO 3, in presence of nitric oxide, NO, in the Chamber Process for sulphuric acid manufacture The proton is a pervasive homogeneous catalyst because water is the most common solventHomogeneous catalysts are in the same physical state as the reactants Usually a homogeneous catalyst is an aqueous catalyst for a reaction between two aqueous solutions It works by combining with the reactants to form an intermediate species, wh



Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia




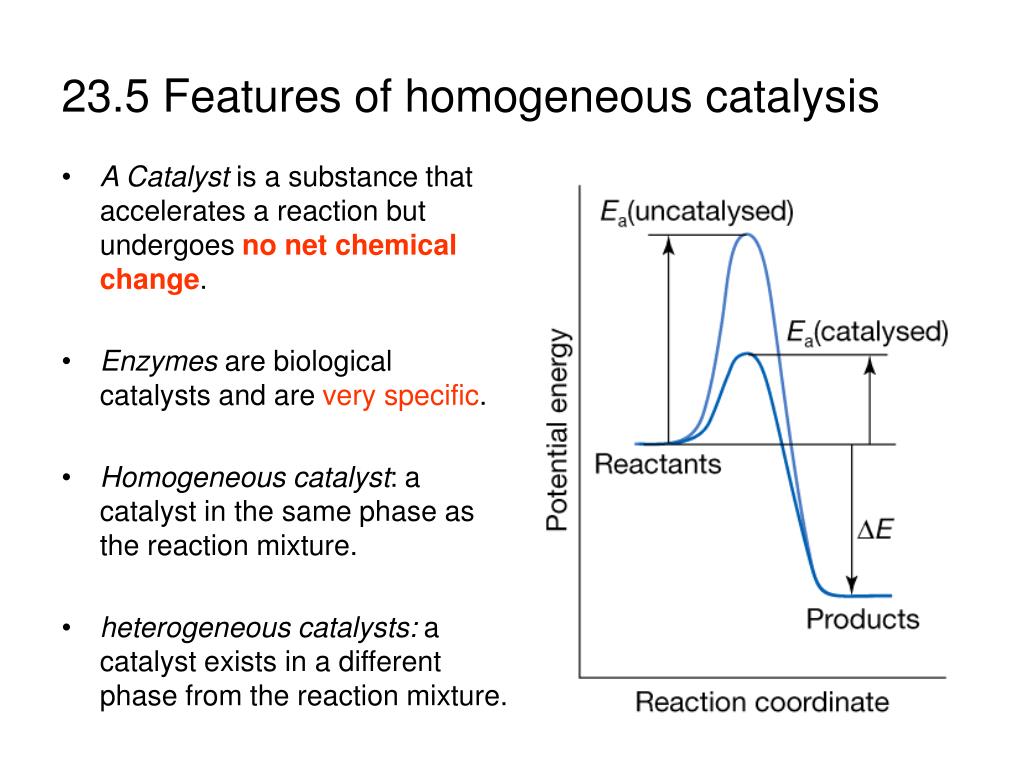
23 5 Features Of Homogeneous Catalysis A Catalyst
An example of a homogeneous catalyst is oxidizing iodide ions with peroxodisulfate ions Iodine can easily be oxidized, and theCatalysis Catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis Many catalytic processes are known in which the catalyst and the reactants are not present in the same phase—that is, state of matter These are known as heterogeneous catalytic reactions They include reactions between gases or liquids or both at the surface of a solid catalyst Since the surface is the place at which the reactionHeterogeneous catalysis in terms of catalytic effectiveness, cata lyst properties, and catalyst separation1 Homogeneous cataly sts offers improved selectivity, increased
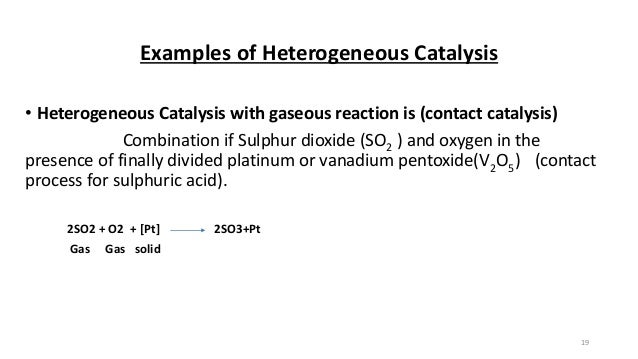



Catalysis



Classify The Following Into Homogenous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
An advantage of homogeneous catalysis is there is a very high degree of interaction between the catalyst and reactant molecules due to both being in the same phase (as opposed to heterogeneous catalysis) A disadvantage is the homogeneous catalyst is often irrecoverable after the reaction has run to completionThe catalyst is not behaving like a conventional homogeneous molecular catalyst but more like the metallic active sites exploited in heterogeneous catalysts 'We still get singlesite Give four examples of heterogeneous catalysis Answer (i) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide to form sulphur trioxide In this reaction, Pt acts as a catalyst (ii) Formation of ammonia by the combination of dinitrogen and dihydrogen in the presence of finely divided iron




The Transformation Strategies Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysts For The Coupling Reactions Of Co2 And Epoxides Olefins Sciencedirect




Comparison Of Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Catalysis Download Table
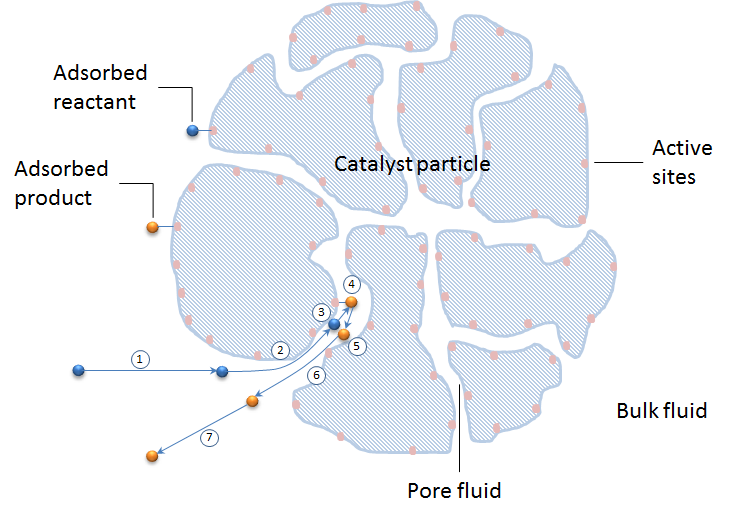
The process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reactants, products and catalyst exist in the same phase Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also immiscible mixtures (eg oil and water ), or anywhere an interface is present Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactantsPersulphate ions (peroxodisulphate ions), S 2 O 8 2, are very powerful oxidising agents Iodide ions are very easily oxidised to iodineHomogeneous catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis 1 When the reactants and the catalyst are in the same phase (ie, liquid or gas), the process is said to be homogeneous catalysisfor example Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide with dioxygenin the presence of oxides of nitrogen as the catalyst in the leadchamber process2SO2(g) O2(g)→NO(g) 2SO3(g) 2




Organometallic Reactions And Catalysis Chapter 14 Gain Or
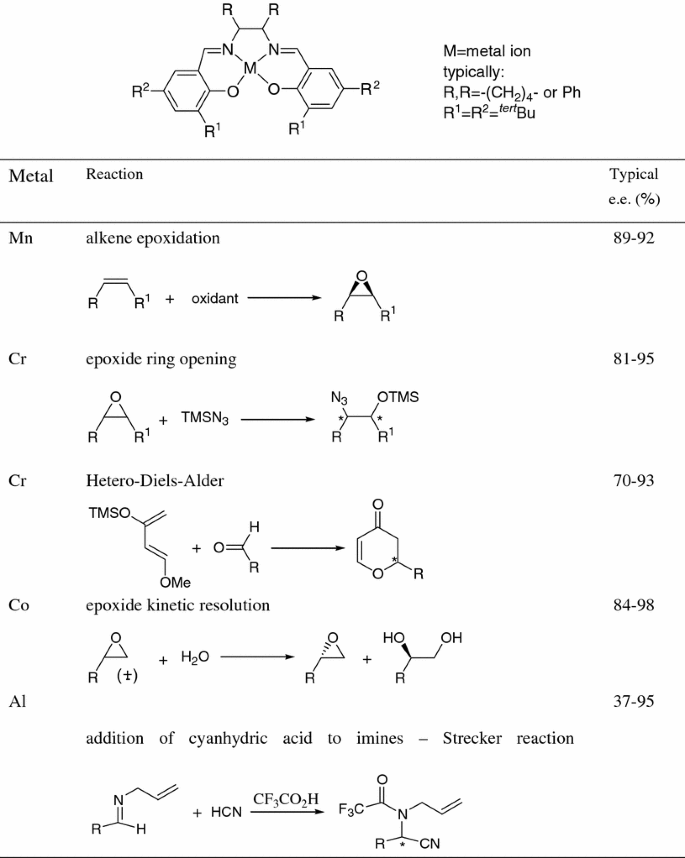



Crossing The Borders Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Developing Recoverable And Reusable Catalytic Systems Springerlink
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis We model catalysis, spectroscopy and photochemistry of molecular systems containing transition metals and also catalytic phenomena involving metal or metaloxide clusters attached to a support, like, for example, a metalorganic framework We focus on various classes of reactions including the conversion of natural gas from Abstract In this Chem issue, Han et al devised a system relying on tandem heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis by ruthenium species for the CO2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons with remarkable In heterogeneous catalysis, the reaction starts at the surface of the solid catalyst and so it is also known as surface catalysis Example Manufacture of H 2 SO 4 by contact process involves oxidation of SO 2 into SO 3 in presence of V 2 O 5 (solid) as catalyst




Ppt On Reaction Kinetics Powerpoint Slides




Which Of The Following Reactions Is An Examples Of Homogeneous Catalysis Youtube
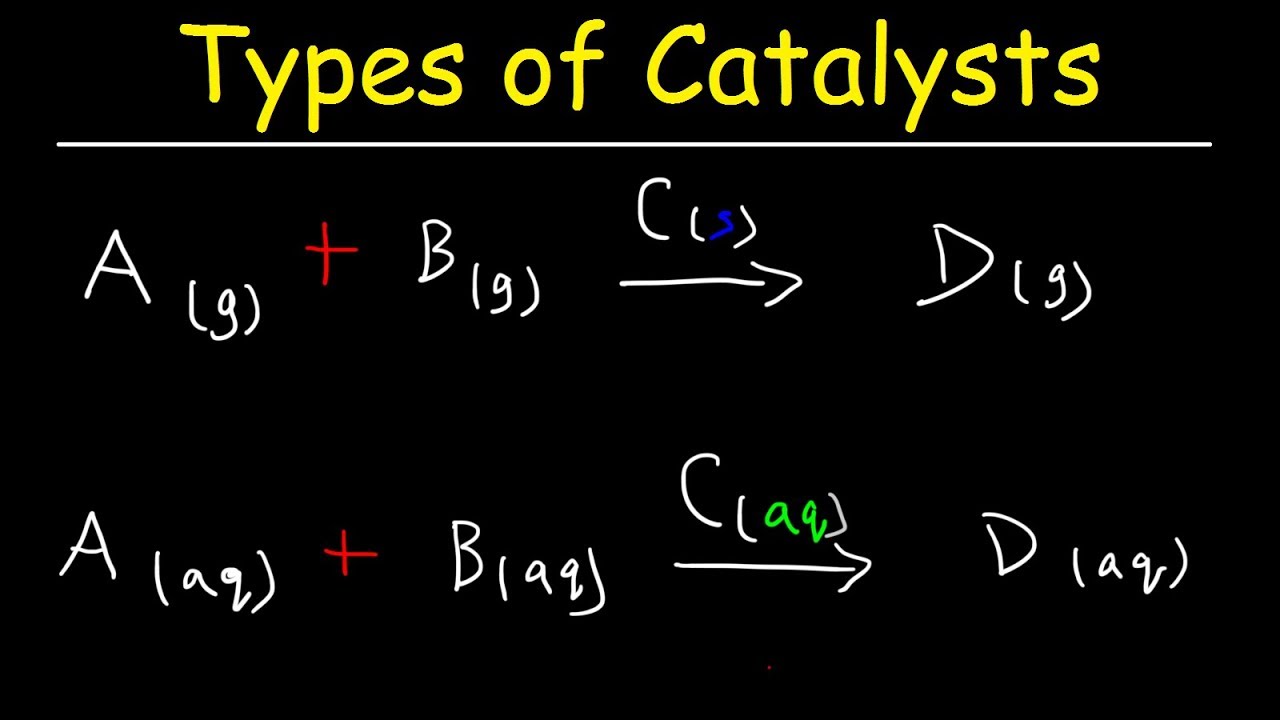
Catalysts can be classified in two types homogeneous and heterogeneous Homogeneous catalysts are those that exist in the same phase (gas or liquid) as reagents, while heterogeneous catalysts are not in the same phase as the reagents Typically, heterogeneous catalysis implies the use of solid catalysts placed in a liquid reaction mixtureCatalysts are generally divided into two types, those that are in the same phase as the reactants (homogeneous catalysts) and those that belong to a different phase (heterogeneous catalysts) The first of the two reactions in this demonstration is an example of a homogeneous catalystHomogeneous vs heterogeneous catalysis Dr habil Marko Hapke 5 5 Heterogeneous Catalysis Major industrial processes using heterogeneous catalysis Process Catalyst Reactants Products Application HaberBosch process Magnetite (Fe) H 2, N 2 NH 3 Fertiliser, explosives Methanol synthesis Cu/ZnO/Al 2O 3 CO, CO 2, H
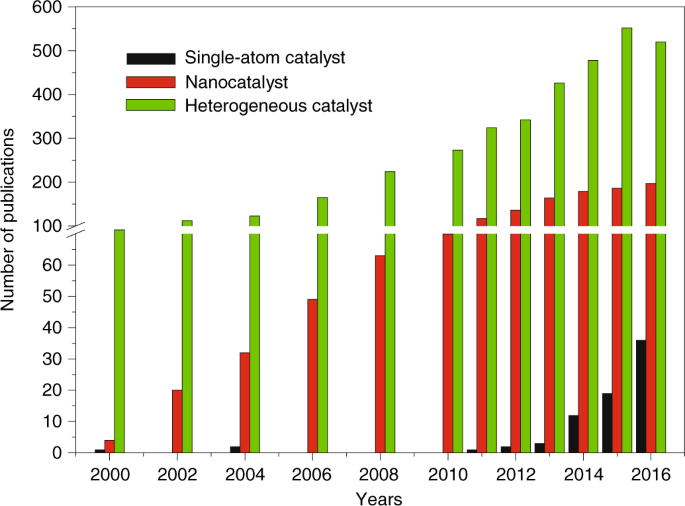



Bridging Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis By Heterogeneous Single Metal Site Catalysts Nature Catalysis




Summarizing Comments On The Discussion And A Prospectus For Urgent Future Action Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences
Examples of Homogeneous Catalysts Acid catalysis, organometallic catalysis, and enzymatic catalysis are examples of homogeneous catalysis Most often, homogeneous catalysis involves the introduction of an aqueous phase catalyst into an aqueous solution of reactants Mechanism of Homogeneous Catalytic Reactions The catalyst combines with one of the reactants to form an intermediate Intermediate compound being unstable either decomposes or combines with the other reactant form the product and the catalyst is regenerated For Example the combination of SO2 and O2 to form SO3 is a slow processThis page looks at the the different types of catalyst (heterogeneous and homogeneous) with examples of each kind, and explanations of how they work You will also find a description of one example of autocatalysis a reaction which is catalysed by one of its products




Homogeneous Catalysis Mpharm Msc Bpharm Bsc




Give Four Examples Of Heterogeneous Catalysis Chemistry Shaalaa Com




Homogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Catalysis Chemical Kinetics




Ch E 553 Lecture 22 Introduction To Catalysis




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia




Homogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia




Diff B W Homogenous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Brainly In
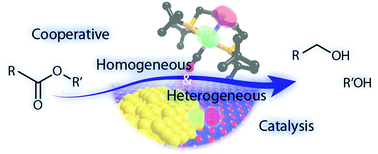



Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Catalysis For The Hydrogenation Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives History Advances And Future Directions Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing
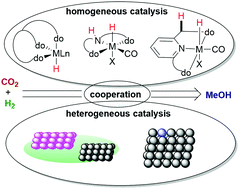



Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysts For Hydrogenation Of Co2 To Methanol Under Mild Conditions Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing
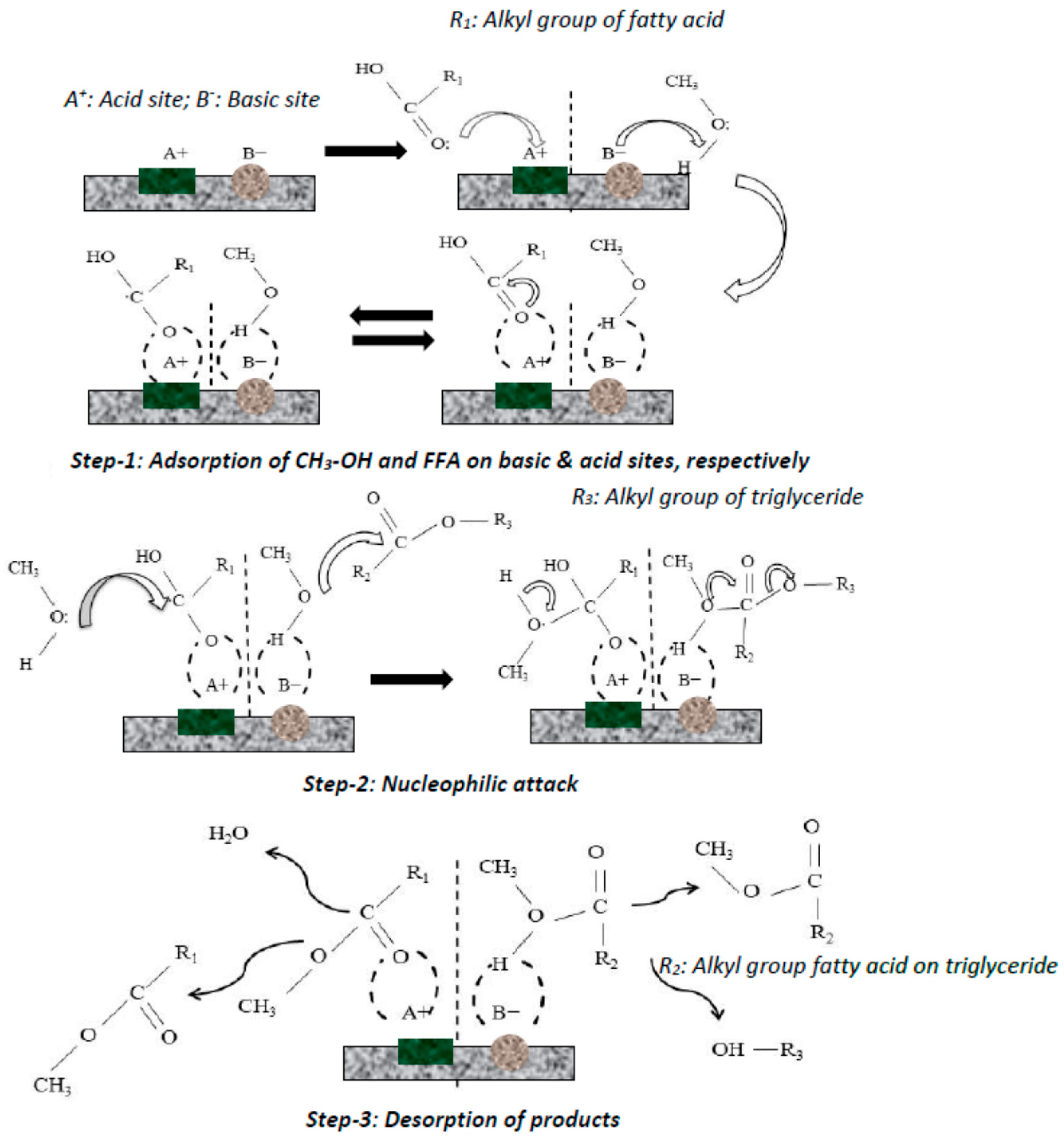



Catalysts Free Full Text Application Of Heterogeneous Catalysts For Biodiesel Production From Microalgal Oil A Review Html
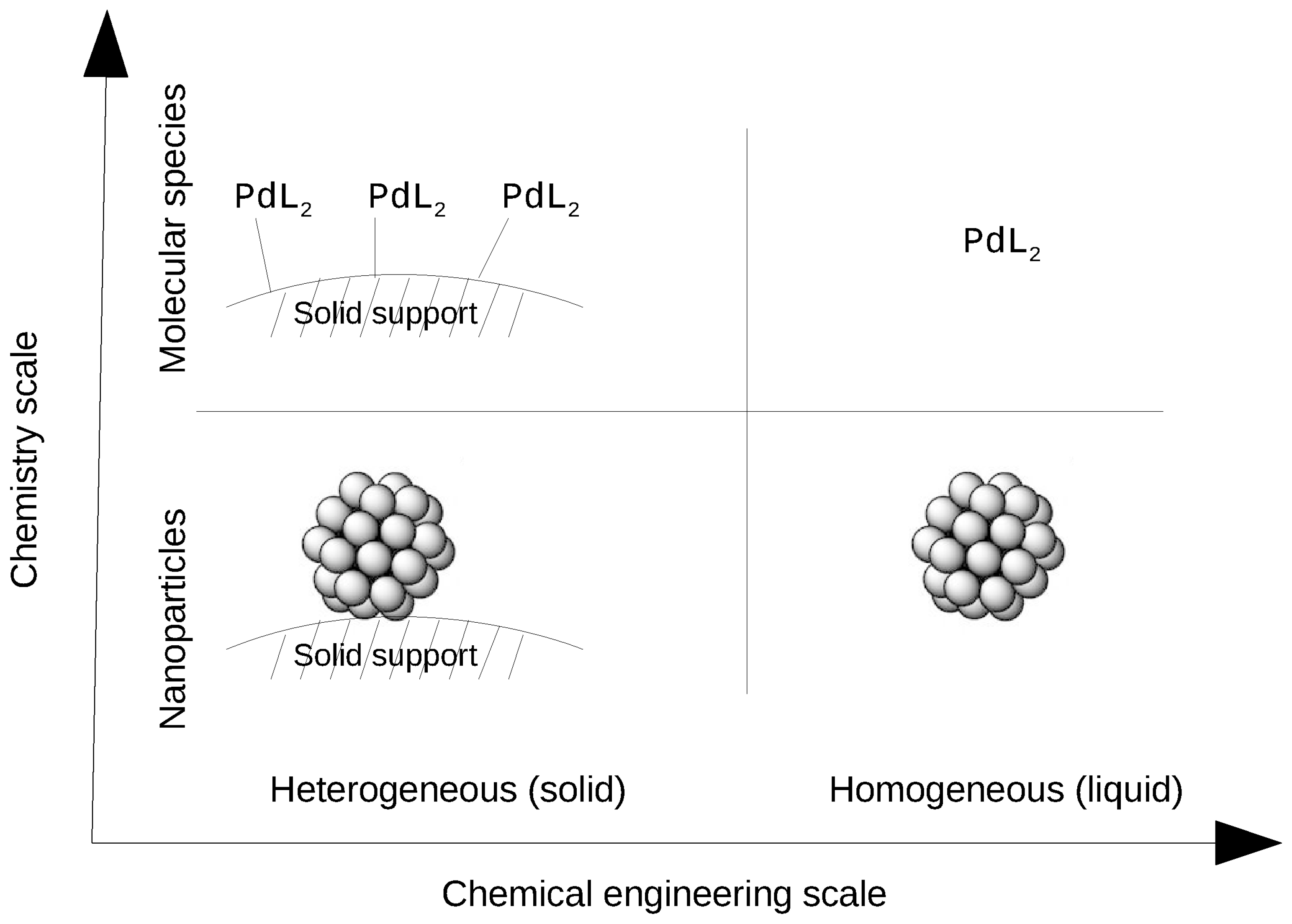



Catalysts Free Full Text About Solid Phase Vs Liquid Phase In Suzuki Miyaura Reaction Html




Membrane Reactors Separating Reactive Gas From The Other Reaction Download Scientific Diagram



10 5 Catalytic Reaction Ppt Video Online Download



1




Combining Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Feature Chemistry World




Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Homogeneous Catalysis




Comparison Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysts Download Scientific Diagram



Ppt 23 5 Features Of Homogeneous Catalysis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Catalysis For The Hydrogenation Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives History Advances And Future Directions Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing




Catalysis Pdf Heterogeneous Catalysis Catalysis




Catalysis Boundless Chemistry



1



Homogeneous Catalysis For The Conversion Of Biomass And Biomass Derived Platform Chemicals Catalysis Science Technology Rsc Publishing
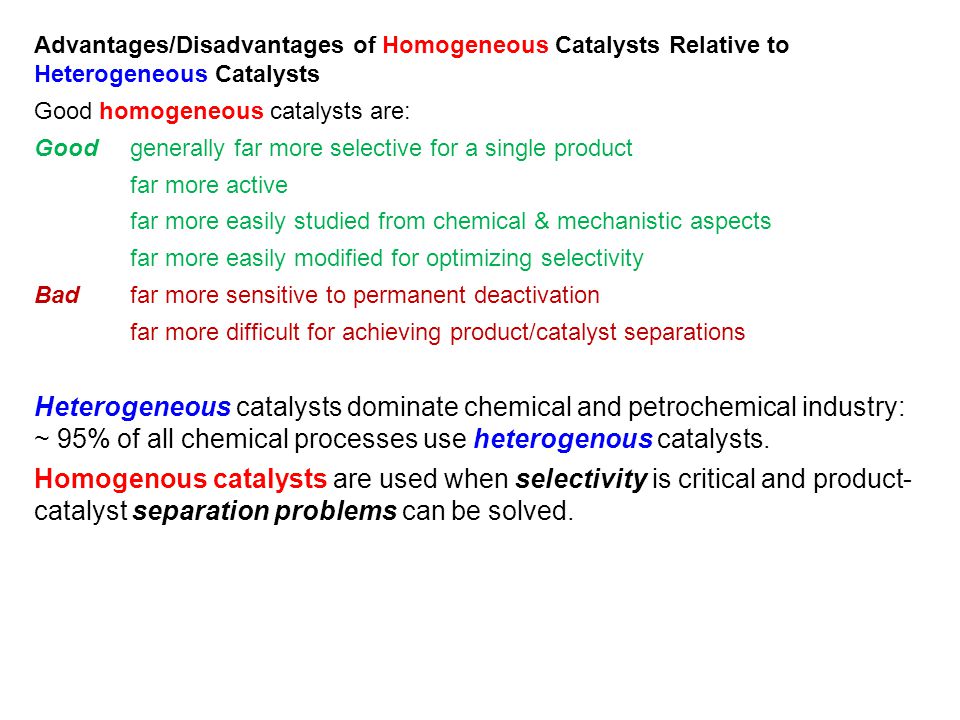



Homogeneous Catalysis Introduction Ppt Video Online Download



Heterogeneous Catalytic Process For Wastewater Treatment Intechopen



How Can Heterogeneous Catalysts Differ From Homogeneous Catalysts Quora



An Overview Of Different Types Of Catalysts Legal Advantage




Homogeneous Catalysis For The Nitrogen Fuel Cycle Pnas



Modeling Approaches In Heterogeneous Catalysis Comsol Blog



Homogeneous Vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Basic Introduction Youtube




Chemistry Heterogeneous Catalysis Handwiki




Special Features Advantages And Disadvantages Of Homo And Download Scientific Diagram
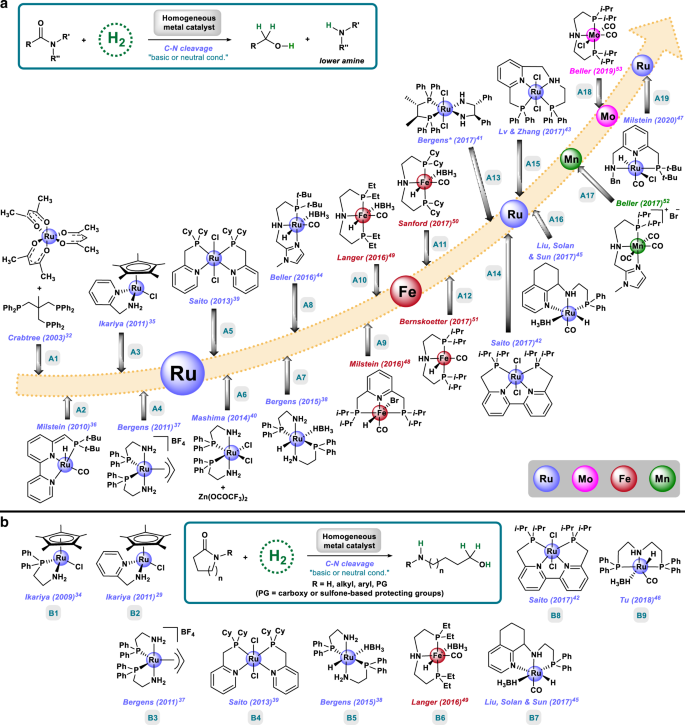



Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalytic Reduction Of Amides And Related Compounds Using Molecular Hydrogen Nature Communications
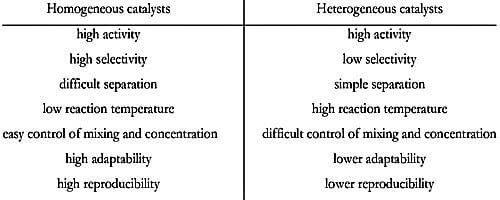



Differences Between Homogeneous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Qs Study
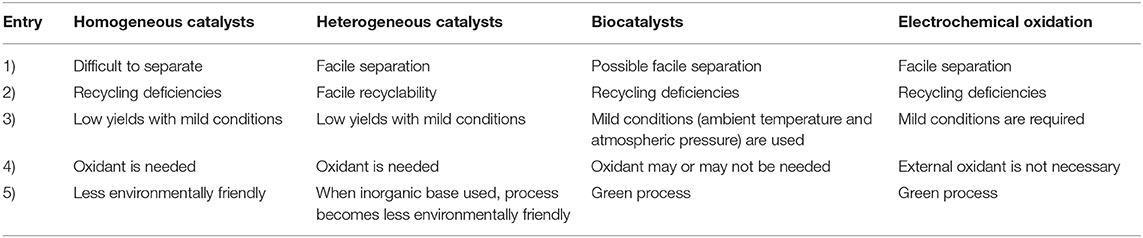



Frontiers Heterogeneous Catalytic Conversion Of Sugars Into 2 5 Furandicarboxylic Acid Chemistry




Navigating Through The Maze Of Homogeneous Catalyst Design With Machine Learning Trends In Chemistry
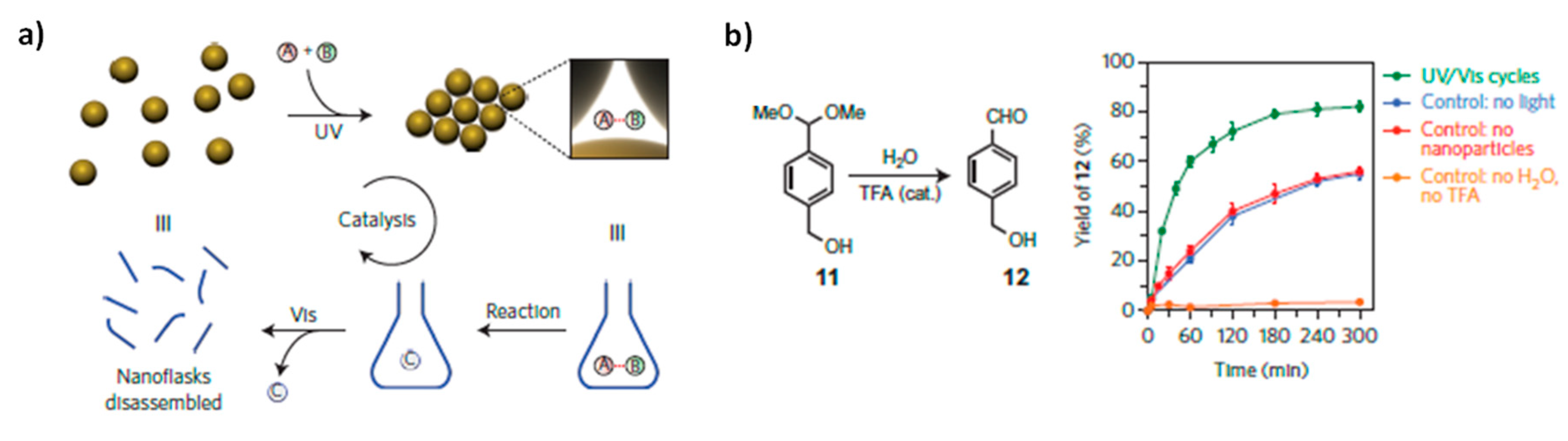



Catalysts Free Full Text Switchable Stimuli Responsive Heterogeneous Catalysis Html



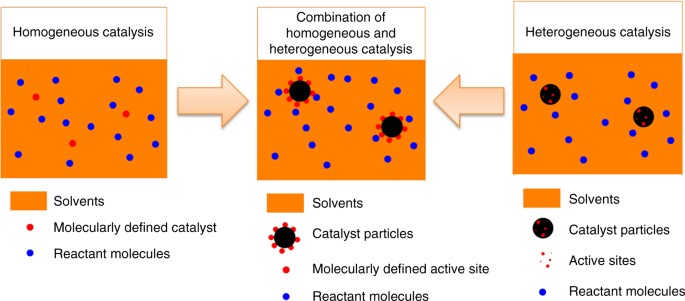
Crossing The Borders Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Developing Recoverable And Reusable Catalytic Systems Springerlink



1



Http Www Ijetsr Com Images Short Pdf 1496 1500 Ieteb410 Ijetsr Pdf




Rate Processes Catalysts Rate Processes In Chemical Reactions Kinetics And Equilibrium Mcat Content
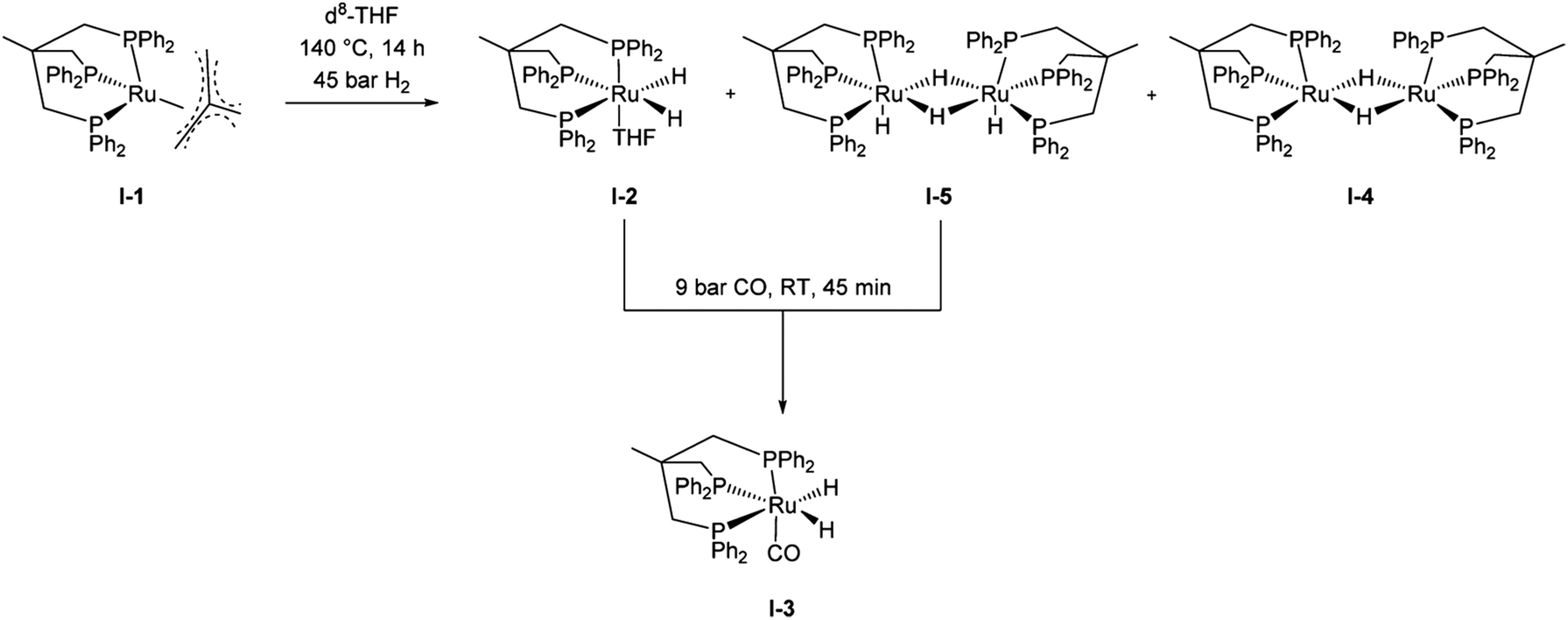



Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Catalysis For The Hydrogenation Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives History Advances And Future Directions Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing




Give Four Examples Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions




Heterogeneous Homogeneous Catalysts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Types Of Catalysis




Homogeneous Catalysis Qs Study




Catalysis Mechanism Types Enzymes Biocatalysts Videos Examples



Web Vscht Cz Bernauem Ark Lectures Chapter 8 Pdf




Which Of The Following Reations Are Examples For Heterogeneous Catalysis Youtube




Difference Between Homogeneous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Surface Chemistry Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctrvbbisy7ikjyh35 8msk3jkudkzizuszlwrim5fn3f2i54ygk Usqp Cau



Direct Arylation Using Heterogeneous Catalysts With Evidence Of Download Scientific Diagram




Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Heterogeneous Catalysis Reaction



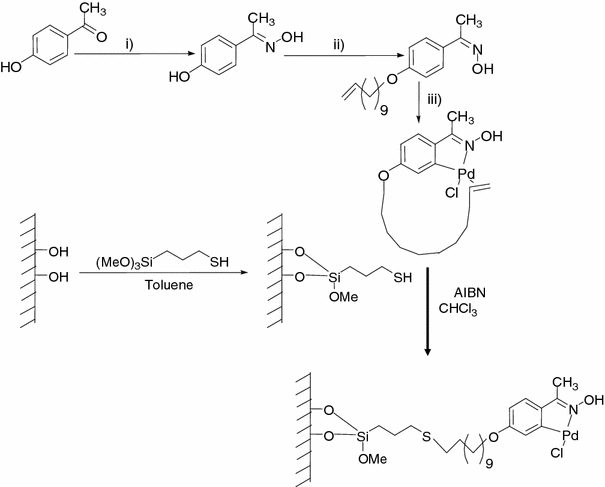
Synthesis Of A Molecularly Defined Single Active Site Heterogeneous Catalyst For Selective Oxidation Of N Heterocycles Nature Communications




Homogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
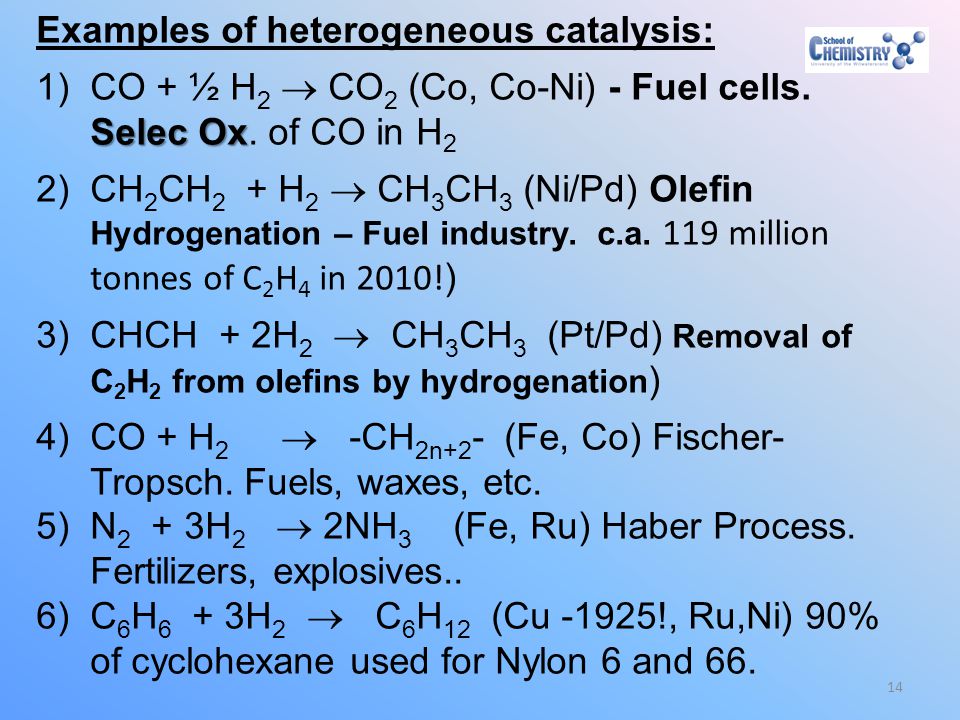



Chemistry 3030 Catalysis Course Ppt Download




Metal Oxides In Heterogeneous Oxidation Catalysis State Of The Art And Challenges For A More Sustainable World Vedrine 19 Chemsuschem Wiley Online Library




Homogeneous Catalyst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Www Ethz Ch Content Dam Ethz Special Interest Chab Icb Van Bokhoven Group Dam Coursework Catalysis 17 Homogeneous Heterogeoenous Catalysis Mesoporousmaterials Pdf



Ppt Heterogeneous Catalysis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




A Review Of The Problem Of Distinguishing True Homogeneous Catalysis From Soluble Or Other Metal Particle Heterogeneous Catalysis Under Reducing Conditions Sciencedirect




Crossing The Divide Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis In Water Oxidation Pnas



Heterogeneous Catalysis Qs Study



Types Of Catalysis Homogeneous Catalysis Heterogeneous Catalysis Positive Catalysis Negative Catalysis Induced Catalysis Acid Base Catalysis
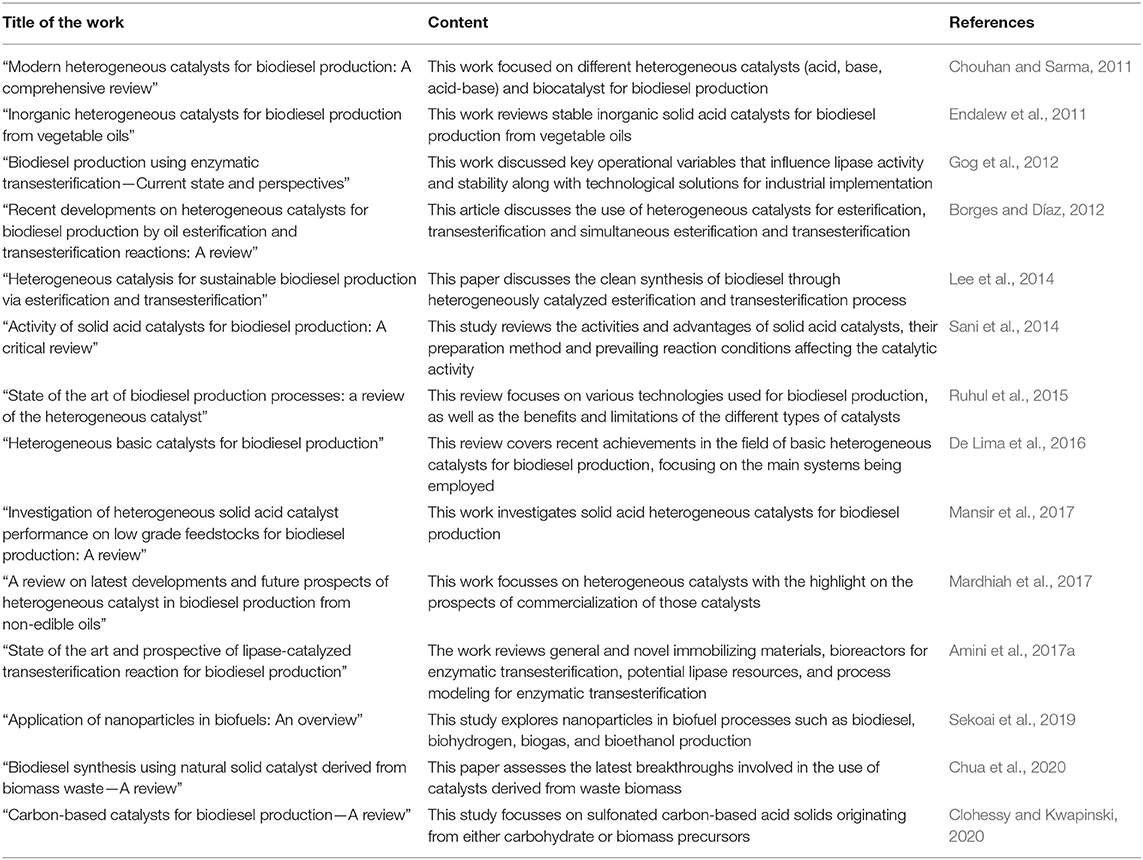



Frontiers State Of The Art Of Catalysts For Biodiesel Production Energy Research
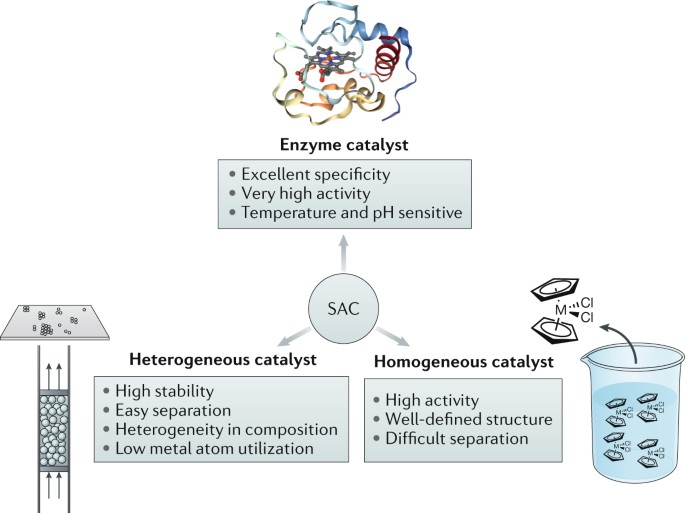



Heterogeneous Single Atom Catalysis Nature Reviews Chemistry



Catalysis Meaning Of Catalyst Its Characteristics And Types




Catalysis Powerpoint Slides



Ethz Ch Content Dam Ethz Special Interest Chab Icb Van Bokhoven Group Dam Coursework Catalysis 17 Homogeneous Heterogeoenous Catalysis Mesoporousmaterials Pdf



Heterogeneous Catalytic Process For Wastewater Treatment Intechopen



Catalysis In Industry




Answers To The Question From Lecture 3 Ppt Download




What Is The Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis




Pdf Combining The Benefits Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis With Tunable Solvents And Nearcritical Water Semantic Scholar



Types Of Catalysis




Similarities And Differences In Hetero And Homogenous Catal By Justyna Kurek
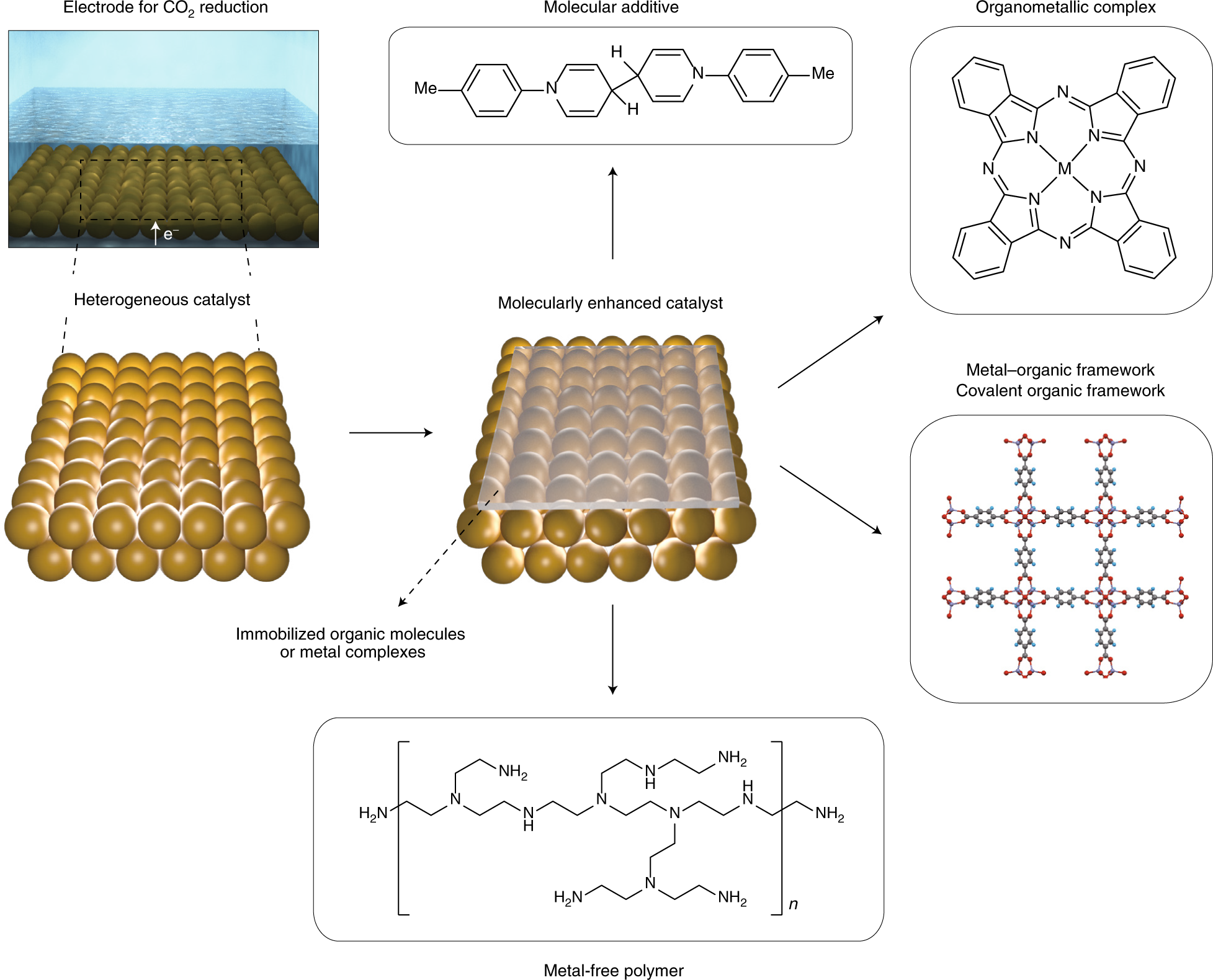



Molecular Enhancement Of Heterogeneous Co2 Reduction Nature Materials




What Are Some Examples Of Homogeneous Catalysis Quora




Pdf Distinguishing Between The Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Mechanisms Of Catalysis In The Mizoroki Heck And Suzuki Miyaura Reactions Problems And Prospects




Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
コメント
コメントを投稿